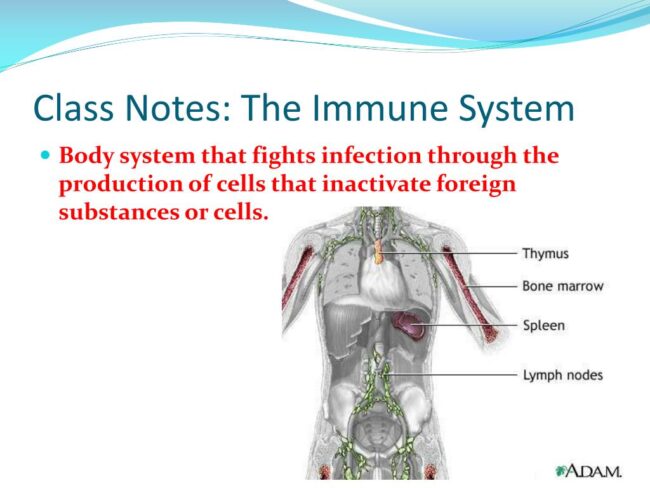
The immune system is a complex network of cells, tissues, and organs that work together to protect the body from harmful pathogens and foreign substances. It is an essential part of our body’s defense mechanism, constantly on the lookout for potential threats.
At the core of the immune system are white blood cells, also known as leukocytes. These cells are produced in the bone marrow and are responsible for identifying and destroying invading pathogens. There are two main types of white blood cells: phagocytes, which engulf and destroy foreign substances, and lymphocytes, which produce antibodies to specifically target and neutralize pathogens.
But how does the immune system know which cells or substances to attack and which to ignore? The answer lies in a fascinating process called immune recognition. The immune system is equipped with specialized molecules, known as antigens, that can recognize specific markers on the surface of invading pathogens. This allows the immune system to distinguish between self (the body’s own cells) and non-self (foreign substances).
While the immune system is designed to protect us, there are several factors that can influence its effectiveness. One such factor is age. As we age, our immune system tends to become weaker, making us more susceptible to infections and diseases. Additionally, certain medical conditions, such as autoimmune disorders, can cause the immune system to malfunction and attack the body’s own cells.
Other factors that can impact the immune system include lifestyle choices, such as diet and exercise. A healthy, balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals is crucial for maintaining a strong immune system. Regular exercise can also help boost immunity by improving circulation and reducing stress. On the other hand, poor diet choices, lack of exercise, and chronic stress can weaken the immune system and make us more prone to illness.
In conclusion, the immune system plays a vital role in defending the body against infections and diseases. Understanding how it works and what factors can influence its effectiveness is key to maintaining optimal health. By making healthy lifestyle choices and taking proactive measures to support our immune system, we can strengthen our body’s natural defense mechanism and enhance our overall well-being.
The differences and peculiarities of innate and adaptive immunity
The immune system is a complex network of cells, tissues, and organs that work together to protect the body from harmful pathogens. There are two major branches of the immune system: innate immunity and adaptive immunity. While both branches function to defend the body against infections, they have distinct differences and peculiarities.
Innate immunity:
| Characteristics | Explanation |
| Non-specific | Innate immunity provides a general defense mechanism against a wide range of pathogens, regardless of their specific nature. |
| Rapid response | Innate immune responses occur quickly after exposure to pathogens, typically within hours. |
| Physical and chemical barriers | It includes physical barriers like skin and mucous membranes, as well as chemical barriers like antimicrobial proteins and enzymes. |
| Inflammatory response | Innate immunity triggers inflammation in response to tissue damage or infection, leading to increased blood flow and recruitment of immune cells. |
| No immunological memory | Innate immunity does not create memory cells, meaning that the response to a pathogen is the same each time it is encountered. |
Adaptive immunity:
| Characteristics | Explanation |
| Specific | Adaptive immunity is tailored to recognize and target specific pathogens. It has the ability to distinguish between different strains of the same pathogen. |
| Slower response | Adaptive immune responses take some time to develop, typically several days, as the immune system needs to recognize the pathogen and mount an appropriate response. |
| Cellular and humoral immunity | Adaptive immunity involves two main types of responses: cellular immunity, mediated by T cells, and humoral immunity, mediated by B cells and antibodies. |
| Immunological memory | Adaptive immunity generates memory cells that “remember” previously encountered pathogens, resulting in a faster and more efficient response upon re-exposure. |
| Vaccine response | Adaptive immunity is responsible for the long-term protection provided by vaccines, as it can create memory cells specific to vaccine antigens. |
While innate immunity serves as the first line of defense against pathogens, adaptive immunity provides a targeted and long-lasting response. These two branches of the immune system work together to maintain the body’s overall health and protect it from infectious diseases.
The structure of the immune system and its functioning principle
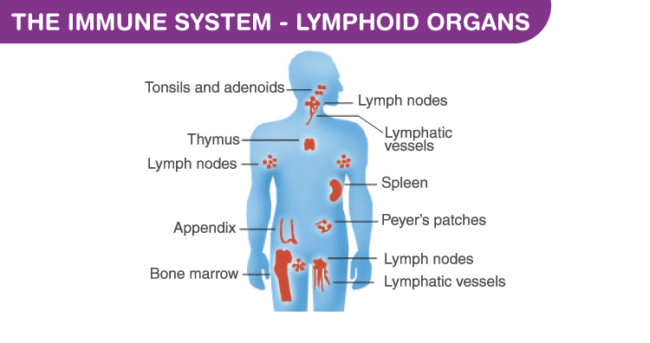
The immune system is a complex network of cells, tissues, and organs that work together to protect the body against viruses, bacteria, and other harmful invaders. It is composed of different components, each with its own specific role in defending the body.
The first line of defense is the innate immune system, which is present from birth and provides immediate, non-specific protection against pathogens. It includes physical barriers, such as the skin, as well as immune cells like phagocytes and natural killer cells. These cells attack and destroy pathogens, preventing them from causing harm to the body.
The second line of defense is the adaptive immune system, which develops throughout our lives as we encounter various pathogens. It is highly specific and has the ability to remember and recognize specific pathogens. This system includes immune cells called lymphocytes, which are divided into B cells and T cells. B cells produce antibodies, while T cells directly attack infected cells.
The immune system also includes lymphoid organs, such as the spleen, thymus, and lymph nodes. These organs play a critical role in the development and activation of immune cells. The lymphatic system, which consists of lymph vessels and lymph nodes, helps transport immune cells and fluid throughout the body.
The functioning principle of the immune system involves a carefully regulated response to pathogens. When the immune system detects a foreign invader, it initiates an immune response. This response involves the production of immune cells and molecules that work together to eliminate the pathogen. Once the pathogen is eliminated, the immune response is resolved, and the immune system returns to a state of rest.
However, sometimes the immune system can malfunction, leading to various immune disorders. Autoimmune diseases occur when the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy cells and tissues in the body. Allergies are another example of immune system dysfunction, where the immune system overreacts to harmless substances like pollen or certain foods.
In conclusion, the immune system is a complex network of cells, tissues, and organs that function together to protect the body from pathogens. It encompasses both the innate and adaptive immune systems, as well as lymphoid organs and the lymphatic system. Understanding the structure and functioning principle of the immune system is essential for maintaining optimal health and preventing immune-related disorders.
Organs and tissues of the immune system
The immune system is a complex network of organs and tissues that work together to protect the body from harmful pathogens and foreign substances. These organs and tissues are responsible for carrying out the various tasks involved in immune response.
The major organs of the immune system include the bone marrow, thymus, spleen, lymph nodes, and tonsils. Each of these organs plays a unique role in the immune response.
| Organ/Tissue | Function |
|---|---|
| Bone marrow | Produces and stores immune cells, such as white blood cells, that are necessary for immune response. |
| Thymus | Plays a crucial role in the development and maturation of T cells, a type of white blood cell that helps coordinate the immune response. |
| Spleen | Filters the blood and removes old or damaged red blood cells. It also helps to mount an immune response by producing immune cells and antibodies. |
| Lymph nodes | Act as filters for the lymph fluid, trapping pathogens and foreign substances. They also contain immune cells that help fight off infections. |
| Tonsils | Part of the body’s first line of defense against pathogens that enter through the mouth and nose. They produce immune cells and antibodies to help prevent infections. |
In addition to these major organs, there are also various tissues throughout the body that contribute to the immune response. These include the skin, which acts as a physical barrier to pathogens, and the mucous membranes, which produce mucus and contain immune cells to help trap and remove pathogens.
Overall, the organs and tissues of the immune system work together in a coordinated manner to identify and eliminate harmful pathogens, providing a vital defense for the body.
Immune system cells
The immune system consists of several types of cells that work together to defend the body against invading pathogens. These cells are constantly patrolling the body, ready to identify and eliminate any foreign substances that may pose a threat.
One of the key players in the immune system is the white blood cell, also known as leukocyte. There are different types of white blood cells, each with a unique role in the immune response. The two main categories of white blood cells are phagocytes and lymphocytes.
Phagocytes are the first line of defense against pathogens. They patrol the body, searching for foreign substances such as bacteria, viruses, and fungi. Once they identify an invader, phagocytes engulf and destroy it through a process called phagocytosis. Neutrophils and macrophages are examples of phagocytes.
Lymphocytes are another type of white blood cell that play a crucial role in the immune response. There are two main types of lymphocytes: B cells and T cells. B cells are responsible for producing antibodies, which are proteins that recognize and bind to specific antigens on pathogens. T cells, on the other hand, directly attack infected cells and regulate the immune response.
Natural killer (NK) cells are another important type of lymphocyte. They are specialized in killing tumor cells and cells infected with viruses through a process called apoptosis. NK cells are part of the innate immune response and act quickly to eliminate threats.
In addition to white blood cells, there are also other cells that support the immune system. These include dendritic cells, mast cells, and eosinophils. Dendritic cells capture and present antigens to lymphocytes, initiating an immune response. Mast cells release substances such as histamine, contributing to inflammation. Eosinophils play a role in defending against parasites and regulating allergic reactions.
The proper functioning of immune system cells is influenced by various factors, including genetics, nutrition, age, stress, and lifestyle. Understanding how these cells work and what factors can influence them is essential for maintaining a strong and effective immune system.
Factors influencing immunity
The immune system is a complex network of cells, tissues, and organs that work together to protect the body against harmful pathogens such as bacteria, viruses, and parasites. While the immune system is designed to function optimally, there are several factors that can influence its effectiveness.
1. Genetics: Genetic factors play a significant role in determining an individual’s immune system strength and response. Certain genetic variations can make a person more susceptible to certain infections or autoimmune diseases.
2. Age: The immune system undergoes changes as we age, which can affect its ability to fight off infections. For example, older adults may have a weaker immune response and may be more prone to certain diseases.
3. Lifestyle: Lifestyle factors such as diet, exercise, and sleep can have a profound impact on the immune system. A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can provide essential vitamins and minerals that support immune function. Regular physical activity can also enhance the immune system’s ability to fight off infections.
4. Stress: Chronic stress has been shown to weaken the immune system and make individuals more susceptible to infections. Stress hormone levels can interfere with immune cell function and reduce the body’s ability to mount an effective immune response.
5. Environmental factors: Exposure to environmental pollutants, toxins, and chemicals can negatively impact the immune system. Air pollution, cigarette smoke, and certain chemicals can compromise the respiratory system, making individuals more susceptible to respiratory infections.
6. Medical conditions: Underlying medical conditions such as diabetes, cancer, and HIV/AIDS can weaken the immune system. These conditions may impair the body’s ability to mount an effective immune response and make individuals more susceptible to infections.
7. Medications: Some medications, such as immunosuppressants and corticosteroids, can suppress the immune system. While these medications may be necessary to manage certain conditions, they can also increase the risk of infections.
It’s important to note that while these factors can influence immunity, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, managing stress, and seeking medical treatment for underlying conditions can help support a strong immune system.
Stress
Stress is a well-known factor that can significantly influence the immune system. When a person experiences stress, the body releases stress hormones, such as cortisol, that have an impact on immune cells. These hormones can suppress the activity of the immune system, making it less efficient in fighting off infections and diseases.
Chronic stress, which is long-term and persistent, can have even more detrimental effects on the immune system. It can lead to a constant release of stress hormones, causing chronic inflammation and weakening the immune response. This can increase the susceptibility to infections and make it harder for the body to recover from illnesses.
Furthermore, stress can also indirectly affect the immune system by influencing behavior and lifestyle factors. For example, when people experience stress, they may be more likely to engage in unhealthy behaviors, such as poor diet, lack of exercise, or insufficient sleep, which can further compromise the immune system.
It is important to note that not all stress is detrimental to the immune system. In fact, short-term stress can have a positive effect by temporarily boosting immune function. This can be seen in the body’s “fight or flight” response, where stress triggers a release of immune cells to quickly respond to potential threats. However, if stress becomes chronic or excessive, it can outweigh these short-term benefits and lead to immune dysfunction.
To maintain a healthy immune system, it is crucial to manage and reduce stress levels. Engaging in stress-reducing activities, such as exercise, meditation, or spending time with loved ones, can help mitigate the negative effects of stress on the immune system. Additionally, adopting healthy lifestyle habits, including a balanced diet, regular physical activity, and sufficient sleep, can also support a strong immune system.
Age
Age plays a crucial role in the functioning of the immune system. As we age, our immune system undergoes changes that can impact its effectiveness in fighting off infections and diseases. One of the most significant changes is a decline in the production of new immune cells, such as T cells and B cells.
This decline in cell production can lead to a weakened immune response, making older individuals more susceptible to infections. Additionally, aging can also affect the ability of immune cells to communicate with each other and mount an efficient response. This can result in a slower and less effective immune response in older adults.
Furthermore, aging can also lead to the accumulation of senescent cells in the body. These cells are no longer able to divide and function properly, and they can release harmful substances that can impair the function of surrounding cells and tissues. The accumulation of senescent cells can contribute to chronic inflammation and weaken the immune system.
Other age-related factors, such as hormonal changes and chronic illnesses, can also influence the immune system. For example, the decline in estrogen levels during menopause can affect the immune response in women. Similarly, conditions like diabetes and obesity can impair immune function.
Overall, age is an important factor to consider when examining the functioning of the immune system. Understanding how age-related changes impact immune responses can help in devising strategies to enhance immune function in older individuals and improve their overall health.
Gut microflora
The gut microflora, or gut microbiota, refers to the complex community of microorganisms that live in the digestive tract. These microorganisms, including bacteria, fungi, viruses, and other microbes, play a crucial role in maintaining a healthy immune system.
The gut microflora helps to digest food, produce essential nutrients, and protect against harmful pathogens. It also plays a vital role in the development and function of the immune system. The microorganisms in the gut interact with immune cells and help to educate and regulate their responses.
Several factors can influence the composition and diversity of the gut microflora. One of the most important factors is diet. A diet high in fiber and natural plant-based foods promotes a healthy gut microbiota, while a diet high in processed foods and saturated fats can disrupt the balance of microbes in the gut.
Other factors that can influence the gut microflora include medications, such as antibiotics, which can disrupt the natural balance of bacteria in the gut. Stress, lack of sleep, and certain medical conditions can also affect the gut microbiota.
- Probiotics: Probiotics are live bacteria and yeasts that can provide health benefits when consumed in adequate amounts. They can help restore the balance of gut microflora and support a healthy immune system.
- Prebiotics: Prebiotics are non-digestible fibers that stimulate the growth and activity of beneficial bacteria in the gut. Foods rich in prebiotics include onions, garlic, bananas, and whole grains.
Research on the gut microflora and its impact on immune function is still evolving. However, maintaining a healthy gut microbiota through a balanced diet and lifestyle choices is generally considered beneficial for overall health and immune system function.
Lifestyle
Lifestyle plays a significant role in the functioning of the immune system. Certain habits and practices can either strengthen or weaken the immune response. Here are some lifestyle factors that can influence the immune system:
- Diet: A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins provides the necessary vitamins and minerals that support immune function. Consuming excessive amounts of sugar and processed foods, on the other hand, can weaken the immune system.
- Exercise: Regular physical activity can enhance immune function by improving blood circulation and promoting the production of antibodies and immune cells. However, excessive exercise or intense training without adequate rest can have the opposite effect and suppress immune function.
- Sleep: Sufficient sleep is crucial for optimal immune system functioning. Lack of sleep or poor sleep quality can weaken the immune response and make individuals more susceptible to infections.
- Stress Management: Chronic stress can negatively impact the immune system. Engaging in stress-reducing activities, such as meditation, yoga, or spending time in nature, can help regulate the immune response.
- Hygiene: Practicing good hygiene, such as regular handwashing, can prevent the spread of pathogens and reduce the risk of infections.
- Substance Use: Excessive alcohol consumption, smoking, and illicit drug use can weaken the immune system and impair its ability to defend against pathogens.
- Environmental Factors: Exposure to pollutants, toxins, and certain chemicals can impair immune function. Maintaining a clean and healthy environment can support the immune system.
- Social Connections: Strong social connections and support networks have been shown to have a positive impact on immune function. Having a fulfilling social life can reduce stress and enhance overall well-being, thus benefiting the immune system.
Adopting a healthy lifestyle that includes a nutritious diet, regular exercise, adequate sleep, stress management, and good hygiene can help support a robust immune system. It is important to be mindful of lifestyle choices and strive for balance in order to optimize immune function.
Sleep
Sleep plays a crucial role in the functioning of the immune system. During sleep, the body produces certain proteins called cytokines that help regulate the immune response. These cytokines are essential for fighting off infections and reducing inflammation.
When we don’t get enough sleep, our immune system becomes weakened. Studies have shown that even a single night of sleep deprivation can result in a decrease in immune function. This makes us more susceptible to infections and can prolong the duration of illness.
In addition to affecting the production of cytokines, lack of sleep can also lead to an increase in stress hormones, such as cortisol. High levels of cortisol can suppress the immune system and make it harder for the body to fight off infections.
On the other hand, getting enough sleep can enhance the immune system’s ability to respond to pathogens. It allows the body to produce and release the necessary antibodies and other immune cells that can help combat infections. Sleep also helps in the recovery process, as it allows the body to repair any damage that might have occurred during the day.
To promote a healthy immune system, it is important to prioritize sleep and establish good sleep habits. This includes maintaining a consistent sleep schedule, creating a comfortable sleep environment, and practicing relaxation techniques before bed. By prioritizing sleep, we can support our immune system and maintain overall good health.
| Factors that can influence sleep: |
|---|
| – Stress |
| – Diet and nutrition |
| – Exercise |
| – Medications |
| – Age |
| – Sleep disorders |
Dream
A dream is a succession of images, ideas, emotions, and sensations that usually occur involuntarily in the mind during certain stages of sleep. Dreams can be vivid, colorful, and sometimes strange or bizarre. They can also be forgotten quickly upon waking up, or they can linger in our memories for a long time.
Scientists are still not completely sure why we dream, but there are several theories that try to explain this phenomenon. Some believe that dreaming is a way for our brains to process and organize information, memories, and emotions from our daily lives. Others think that dreams serve as a form of problem-solving or creative thinking, allowing us to explore different scenarios and possibilities.
During dreaming, our bodies are typically in a state of REM (rapid eye movement) sleep. This stage of sleep is characterized by the rapid movement of the eyes, increased brain activity, and vivid dreaming. It is believed that REM sleep is important for memory consolidation and emotional regulation.
Dreams can encompass a wide range of themes and symbols, and they can vary greatly from person to person. Some dreams may reflect our inner desires, fears, or unresolved conflicts, while others may be influenced by external factors such as recent experiences, movies, or books.
Although dreams are often seen as mysterious or even supernatural, they are a natural and normal part of the sleep cycle. While some dreams may seem bizarre or nonsensical, they can provide valuable insights into our subconscious mind and help us better understand ourselves.
Question-answer:
What is the immune system?
The immune system is a complex network of cells, tissues, and organs that work together to protect the body against harmful pathogens such as bacteria, viruses, and parasites.
How does the immune system work?
The immune system recognizes foreign substances in the body and activates an immune response to eliminate them. It consists of two main components: the innate immune system and the adaptive immune system.
What are the different factors that influence the immune system?
There are many factors that can influence the immune system, including age, genetics, nutrition, lifestyle choices (such as smoking or excessive alcohol consumption), stress, sleep patterns, and underlying health conditions.
Can a weakened immune system be strengthened?
Yes, there are several ways to strengthen the immune system. These include maintaining a healthy lifestyle, eating a balanced diet, getting regular exercise, managing stress levels, getting enough sleep, and avoiding exposure to harmful substances.
Reviews
Oliver
As a reader, I found this article on how the immune system works and what factors influence it to be incredibly informative. It provided a clear and concise explanation of the immune system’s function and gave insight into the various factors that can influence its effectiveness. As a male reader, I was particularly interested in learning about the impact of lifestyle choices, such as diet and exercise, on immune system health. It was fascinating to discover that maintaining a healthy lifestyle can boost our immune system’s ability to fight off infections and diseases. I also appreciated the article’s discussion on the role of age, stress, and sleep in immune system function. This article served as a reminder of the importance of taking care of our overall health and well-being to support our immune system. Overall, I found this article to be a valuable resource for understanding how our immune system works and how we can enhance its performance.
Maximus
This article provides a comprehensive explanation of how the immune system works and the various factors that can influence its function. As a male reader, I found it to be quite informative and relevant to my own health concerns. Understanding how the immune system operates is crucial in maintaining good health and preventing illnesses. I particularly appreciated the section that discussed the different components of the immune system, such as white blood cells, antibodies, and lymph nodes. It gave me a better understanding of how these elements work together to defend the body against pathogens and foreign substances. Learning about the body’s natural defense mechanisms was fascinating, and it made me appreciate the complexity of our immune system. Moreover, the article emphasized the importance of maintaining a healthy lifestyle to support a strong immune system. It highlighted factors such as nutrition, exercise, sleep, and stress management as key influencers. This information served as a timely reminder for me to prioritize my well-being by eating a balanced diet, engaging in regular physical activity, and practicing stress-reducing techniques. I also found the discussion on external factors that can impact immunity, such as environmental pollutants and certain medications, to be eye-opening. It made me more aware of potential hazards in my surroundings and how they can affect my immune system’s ability to function optimally. This knowledge will definitely influence my choices and motivate me to create a healthier environment for myself. In conclusion, this article provided a clear and concise overview of how the immune system works and the factors that can influence its performance. As a male reader, I found it to be educational and thought-provoking. It encouraged me to take better care of my immune system by adopting a healthier lifestyle and being mindful of external influences. Overall, I appreciate the valuable insights this article has provided.
Jason Smith
Great article! As a male reader, I found it very informative and engaging. The immune system is such a fascinating and essential part of our bodies, and it’s crucial to understand how it works and what factors influence it. The article did a great job explaining the different components of the immune system, from white blood cells to antibodies, and how they work together to protect us from pathogens. I particularly appreciated the section on factors that can influence the immune system. It’s interesting to learn that factors like stress, diet, sleep, and exercise can all play a role in either boosting or weakening our immune system. As someone who values a healthy lifestyle, it’s a good reminder to prioritize things like regular exercise and a balanced diet to keep my immune system strong. The article also touched on how age and genetics can impact our immune system, which I found intriguing. It’s fascinating to think that some people may be naturally predisposed to having a stronger immune system. Overall, I thoroughly enjoyed reading this article. It was well-written, clear, and provided a lot of valuable information about how the immune system works and what factors can influence it. I feel like I have a better understanding of my own immune system now and will definitely be more conscious of the lifestyle choices I make to support its health. Thanks for sharing this informative piece!
